Cross-platform frameworks vs. native code development
Native apps have long been held at a higher standard than cross-platform apps. However, the truth is cross-platform frameworks development has revolutionized the mobile app industry. Thanks to this approach, developers can create native-like apps for devices using different operating systems, like Android or iOS, at the same time. This translates into lower costs, shorter time to market and, therefore, maximized profits. So, is one actually better than the other? What are the main differences? And what are your options as a developer? These are some of the questions we’ll cover in this article.
What are native apps?
A native app is one that is developed using the language of choice of a given operating system. It’s the traditional way to build apps where Android apps are built using Java and iOS apps are developed using Swift or Objective-C.
What are cross-platform apps?
Cross-platform apps are not necessarily created with the language of choice of a certain operating system. In fact, they can be developed with a variety of frameworks that use the same language and codebase to make the app compatible with multiple operating systems.
Cross-platform vs. native code development

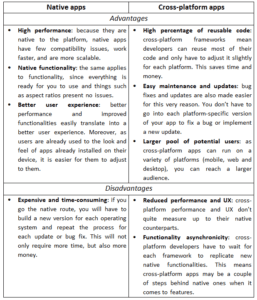
Let’s take a look at the main differences, pros and cons of native and cross-platform development.
Most popular cross-platform frameworks
Now that we’ve looked at each option in detail, let’s take a look at some of the most popular cross-platform frameworks. According to Stack Overflow’s 2020 Developer Survey, these are Flutter, React Native and Xamarin.
Flutter

As stated on its website, Flutter is “Google’s portable UI toolkit for building beautiful, natively-compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase”. Flutter helps you swiftly craft high-quality interfaces for both iOS and Android.
Flutter is not just a framework but a complete SDK, which means it grants users everything they need to create cross-platform apps, such as ready-made widgets, a rendering engine, and testing and integration APIs. The framework works with existing code, is used by developers and organizations around the globe, and is free and open-source.
Flutter also includes widget customization and extensions, its own development language called Dart, an automated testing toolset, and plenty of debugging tools. Some of the development companies currently using Flutter include Groupon, eBay, Alibaba Group and Capital One. You can learn more about Flutter here.
React Native

React Native is an open-source JavaScript development framework that uses ReactJS to create user interfaces for iOS and Android devices. It was developed by Facebook and released in 2013. Facebook not only used it to develop its flagship app, but also others such as Instagram.
With React Native, your JavaScript codebase is compiled to a mobile app nearly indistinguishable from a native iOS app built using Objective-C or a native Android app built using Java. The framework also lets you write modules in other languages such as Swift, Python and C++.
If that wasn’t enough, React Native helps you build your app faster with hot reloading. This feature means you reload your app instantly instead of recompiling after making changes and it even lets you run new code while retaining your application state.
You can learn more about React Native here.
Xamarin

Xamarin, which is owned by Microsoft, is also open-source and works on the “write once, run anywhere” (WORA) model. It uses C# as a single language (which means you don’t have to learn Swift, Objective-C or Java) and harnesses the power of the .NET platform to build native and performant apps for Android, iOS and Windows.
Xamarin can be tested on multiple devices by using cloud services and also includes native API access and native UI support. This framework lets you include Objective-C, Java and C++ libraries, in addition to its considerable collection of class libraries.
Some of the mobile apps created with Xamarin include Azure App, Alaska Airlines and BBVA.
Final thoughts on Cross-platform frameworks vs. native code
Both cross-platform and native code development have their pros and cons. At the end of the day, it all comes down to where your priorities lie. If you prefer not to worry about performance and functionality and have the cash and time to spare, native is the way to go. However, if you are short on budget, want your app to hit the market as soon as possible and are not that bothered by prime app performance, cross-platform is the right choice for you. If that’s so, you can take a look at even more cross-platform frameworks here.